Example: RoundProgressBar
These Example codes are written using the PySide2 Python Package, but the same codes can be written using the PyQt5, the only difference made in the code is in the import statements rest all work the same.
1. Default Round Progress Bar
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar #IMPORT THE EXTENSION LIBRARY
x = 0
p = 1
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
self.hello = 'Round Progress Bar'
self.button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("Click me to change Value")
self.text = QtWidgets.QLabel("Round Progress Bar")
self.text.setAlignment(QtCore.Qt.AlignCenter)
#CREATING THE ROUND PROGRESS BAR OBJECT
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.text)
self.layout.addWidget(self.button)
# ADDING THE ROUND PROGRESS BAR OBJECT TO THE # BOTTOM OF THE LAYOUT
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
self.button.clicked.connect(self.magic) #BUTTON PRESSED EVENT
def magic(self):
global x, p
x = x + 10*p
if x==100:
p = -1
elif x==0:
p = 1
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(x) #CHANGING THE VALUE OF THE PROGRESS BAR
out_text = 'Round Progress Bar: ' + str(x) + '%'
self.text.setText(out_text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Output:
In this demo, we first created an object of the Round Progress Bar:
self.rpb = roundProgressBar() #CREATING THE ROUND PROGRESS BAR OBJECT
After that calling the Round Progress Bar object to display the value of progress using:
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(x) #CHANGING THE VALUE OF THE PROGRESS BAR
The rpb_setValue(value) takes an int as an argument and updates to change the value of the progress bar to the value given.
2. Minimum, Maximum, and Range
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
#IMPORTING THE MODULE
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
#CLASS INSTANCE
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb2 = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb3 = roundProgressBar()
#SETTING THE RANGE :
self.rpb.rpb_setMaximum(720)
self.rpb2.rpb_setRange(0, 720)
self.rpb3.rpb_setRange(0, 1000)
#SETTING THE VALUE
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(456)
self.rpb2.rpb_setValue(456)
self.rpb3.rpb_setValue(890)
self.layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb2)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb3)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
The Maximum and Minimum values of the progress bar can be set using the method: rpb_setMaximum(), and rpb_setMinimum(). By default, the maximum value is set to 100, and the minimum to 0. This can be changed as users use cases. The same result can be achieved by the user using the function: rpb_setRange(). The range function takes two parameters: minimum and maximum in order.
3. Changing the Progress Bar Style
The Round Progress Bar Class has 6 types of different types of Round Progress bar, the default is the Donet type of progress bar which you see in the above example, the other types are illustrated in the image below:
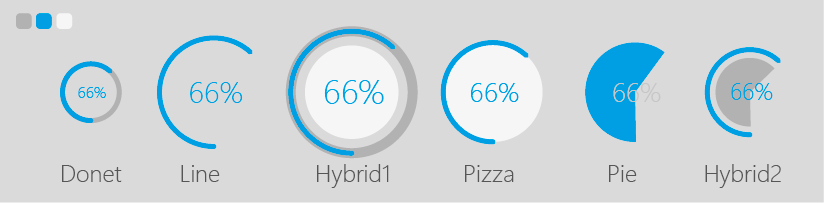
To change the Progress Bar style, use the function:
self.rpb_setBarStyle(Style_Name)
where the different style names are:
Style_Nmae:
Donet (Default)
Line
Pie
Pizza
Pie
Hybrid1
Hybrid2
Example:
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb.rpb_setBarStyle('Pizza') #CHANGE THE BAR STYLE TO : 'Pizza'
self.layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Output:
4. Change the Progress Bar Colors
For changing the progress bar style a few things should be kept in mind: The progress bar is divided into Five parts: Line, Path, Circle, Pie, Text
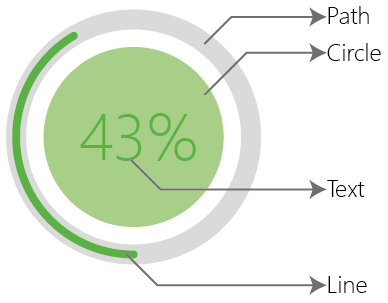
For each parts, we have the following variable which can be changed: Color, Width, Size, Cap, Stroke e.t.c from which the color settings are demonstrated below.
#Line:
object.rpb_setLineColor((R, G, B)) #ARGUMENT RGB AS A TUPLE
#Path:
object.rpb_setPathColor((R, G, B)) #ARGUMENT RGB AS A TUPLE
#Text:
object.rpb_setTextColor((R, G, B)) #ARGUMENT RGB AS A TUPLE
#Circle:
object.rpb_setCircleColor((R, G, B)) #ARGUMENT RGB AS A TUPLE
#Pie:
object.rpb_setPieColor((R, G, B)) #ARGUMENT RGB AS A TUPLE
5. Starting Position
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
#IMPORTING THE PACKAGE
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
#CREATING THE ROUNDPROGRESSBAR CLASS INSTANCE
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb2 = roundProgressBar()
#DEFINING THE INITIAL POSITION OF THE PROGRESS BAR
self.rpb.rpb_setInitialPos('South') #START FROM SOUTH
self.rpb2.rpb_setInitialPos('East') #START FROM EAST
#LAYOUT OF THE PROGRESS BAR
self.layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb2)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
-
A progress bar can have 4 starting positions:
North,South,East, andWest. By default the position isNorth. Users can change the position by using the method:rpb_setInitialPos(), which takes a parameter if position string.self.rpb.rpb_setInitialPos('West') #WEST AS STARTING POSITION.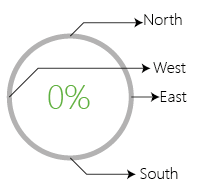
6. Direction of Progress
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
#IMPORTING THE MODULE
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
#CLASS INSTANCE
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb2 = roundProgressBar()
#CHANGING THE DIRECTION
self.rpb.rpb_setDirection('Clockwise')
self.rpb2.rpb_setDirection('AntiClockwise')
#SETTING THE VALUE
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(56)
self.rpb2.rpb_setValue(88)
self.layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb2)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
- The direction of progress denotes the moving direction of the progress bar. By default, it is
Clockwise, which can be changed by the method:rpb_setDirection()which accepts a string corresponding to the direction:ClockwiseandAntiClockwise. It may raise anExceptionif the string is not matched.
7. Text Properties
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
#IMPORTING THE MODULE
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
#CLASS INSTANCE
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb2 = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb3 = roundProgressBar()
#SETTING THE RANGE : MIN-0 & MAX:360
self.rpb.rpb_setRange(0, 360)
self.rpb2.rpb_setRange(0, 360)
self.rpb3.rpb_setRange(0, 360)
#CHANGING THE STYLE
self.rpb.rpb_setBarStyle('Pizza')
self.rpb2.rpb_setBarStyle('Hybrid2')
#CHANGING THE TEXT TYPE : VALUE OR PERCENTAGE
self.rpb.rpb_setTextFormat('Value')
self.rpb2.rpb_setTextFormat('Percentage')
#CHANGING THE TEXT SIZE
self.rpb.rpb_setTextRatio(3)
self.rpb2.rpb_setTextRatio(9)
#CHANGING THE FONT
self.rpb.rpb_setTextFont('Arial')
self.rpb2.rpb_setTextFont('Times New Roman')
#TEXT HIDDEN
self.rpb3.rpb_enableText(False)
#SETTING THE VALUE
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(156)
self.rpb2.rpb_setValue(156)
self.layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb2)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb3)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
This Example contains all the info that is needed for customization of the text inside the progress bar. It contains the following elements:
- Text Format
Text format denotes the format which should be used to display the output value of the progress bar. It can be a Value or a Percentage. From the above image, the first two progress bar has the same rpb_setValue of 156, but one is in Percentage and the other in Value. This may come in handy in certain situations. By default, the format is set to Percentage. The format can be set using the function: rpb_setTextFormat(), which accepts a string.
#CHANGING THE TEXT TYPE : VALUE OR PERCENTAGE
self.rpb.rpb_setTextFormat('Value')
self.rpb2.rpb_setTextFormat('Percentage')
- Text Ratio
The text format signifies the size of the text concerning the size of the progress bar. It can range from 1/3 to 1/50 of the size of the progress bar. This method functions differently from the method rpb_setTextWidth() as the width increase the width of the text but it remains a constant when the size of the round progress bar size changes during the change in window size. This function rpb_setTextRatio() however increases the width concerning the real-time size of the round progress bar. This is demonstrated by the second image in the example. The second example picture contains the enlarged window. The method takes an int and sets it as the ratio.
#CHANGING THE TEXT SIZE
self.rpb.rpb_setTextRatio(3) #1/3 OF SIZE OF THE PROGRESSBAR
self.rpb2.rpb_setTextRatio(9) #1/9 OF SIZE OF PROGRESS BAR
- Text Font
The text inside the round progress bar has a default font: Segoe UI. This can be changed as shown in the example. It can have any standard font installed on the user’s PC. The method used to change the font is rpb_setTextFont() and takes the name of the font as the parameter.
#CHANGING THE FONT
self.rpb.rpb_setTextFont('Arial')
self.rpb2.rpb_setTextFont('Times New Roman')
- Disable Text
By default, the text is Enabled, but users can hide the text using the function: rpb_enableText(), which accepts a bool.
#TEXT HIDDEN
self.rpb3.rpb_enableText(False) #SEE THE IMAGE OF 3RD ROUNDPROGRESSBAR
8. Line Properties
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
#IMPORTING THE MODULE
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
#CLASS INSTANCE
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb2 = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb3 = roundProgressBar()
#LINE WIDTH
self.rpb.rpb_setLineWidth(10)
#LINE CAP
self.rpb.rpb_setLineCap('RoundCap')
self.rpb2.rpb_setLineCap('SquareCap')
self.rpb3.rpb_setLineCap('RoundCap')
#LINE STYLE
self.rpb3.rpb_setLineStyle('DotLine')
self.rpb2.rpb_setLineStyle('DashLine')
#SETTING THE VALUE
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(85)
self.rpb2.rpb_setValue(85)
self.rpb3.rpb_setValue(85)
self.layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb2)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb3)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
The line has many customizable properties each of them is listed below.
- Line Width
Line width is the width of the line that display the progress. It is set to 5px default. The user can use the method rpb_setLineWidth() and pass the desired width in px as an int as the parameter.
#LINE WIDTH
self.rpb.rpb_setLineWidth(10)
- Line Cap
Line cap is the end of the stroke of the line. It can have two styles: RoundCap and SquareCap. The desired cap can be passed as a string to the method: rpb_setLineCap() which takes a string as a parameter. The image above gives a note on how the cap looks.
#LINE CAP
self.rpb.rpb_setLineCap('RoundCap')
self.rpb2.rpb_setLineCap('SquareCap')
self.rpb3.rpb_setLineCap('RoundCap')
- Line Style
The line can be continuous SolidLine or can have a style: DashLine or a DotLine. Each of these styles can be passed as a string to the method: rpb_setLineStyle(). In the image, you can spot the difference between the three styles.
#LINE STYLE
self.rpb3.rpb_setLineStyle('DotLine')
self.rpb2.rpb_setLineStyle('DashLine')
9. Path Properties
import sys
from PySide2 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
#IMPORTING THE MODULE
from PySide2extn.RoundProgressBar import roundProgressBar
class MyWidget(QtWidgets.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)
#CLASS INSTANCE
self.rpb = roundProgressBar()
self.rpb2 = roundProgressBar()
#CHANGING THE PROGRESSABR STYLE
self.rpb.rpb_setBarStyle('Hybrid1')
#CHANGING THE LINE WIDTH
self.rpb.rpb_setLineWidth(3)
self.rpb2.rpb_setLineWidth(8)
#PATH WIDTH
self.rpb.rpb_setPathWidth(15)
self.rpb2.rpb_setPathWidth(2)
#CHANGING THE PATH COLOR
self.rpb.rpb_setPathColor((125, 255, 255))
self.rpb2.rpb_setPathColor((0, 0, 0))
#SETTING THE VALUE
self.rpb.rpb_setValue(85)
self.rpb2.rpb_setValue(85)
self.layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb)
self.layout.addWidget(self.rpb2)
self.setLayout(self.layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
widget = MyWidget()
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
The Path has 3 properties that can be changed and also the path is present in only two styles of the round progress bar: Hybrid1 and the Donet styles. The following methods to modify the path is described below:
- Path Width
Similar to the line width corresponding to the line thickness in px, the path width corresponds to the thickness of the path. Path thickness by default is set to the thickness of the line. But changing it will result in some significant design gains. The method: rpb_setPathWidth() is used for setting the path width. It takes an int as a parameter and it should correspond to the width in px.
- Path Color
Path color method help to change the color of the path of the round Progress Bar path. The method : rpb_setPathColor() accepts a tuple in format: (R, G, B).
#CHANGING THE PATH COLOR
self.rpb.rpb_setPathColor((125, 255, 255)) #CYAN
self.rpb2.rpb_setPathColor((0, 0, 0)) #BLACK COLOR
Also See: Class RoundProgressBar